You may have noticed that your email's been going straight to spam lately. Well, that's because spammers are disguising their malicious emails as if they're coming from a trusted brand. That's why it's so important to use an email authentication tool. For example, Gmail and Outlook providers, like other mailbox providers, need to be confident that messages are legitimate before they're released to the inbox.
The practice of phishing, or pretending to send email from your domain, is a sneaky trick that spammers use to steal your customers' personal information. This is not only a bad experience for them but also damages the perception of your business. Once people realize the communication they received was not legitimate, they will lack trust in future messages and your brand as a whole.
In today’s digital world, email authentication is a must-do for reputable brands to maintain their online reputation with customers. It can be tricky, but it’s imperative that any web application that sends email has this as a top priority. Here’s how:
Be consistent with sender addresses
You've made a mistake and your subscriber opened the message. How do you make sure they don't fall victim to phishing scams? The first step is to be consistently inviting and user-friendly language. You might be tempted to change up your tone, but that can make recipients warier and reject your messages. This can lead to lower engagement rates, higher bounce rates, and general consumer dissatisfaction.
Also, a domain name is crucial. You can’t be using your cousin’s account or a slight variation of your website. This is because it might break trust with your subscribers and they will be more prone to phishing scams. For example, if your original domain is example.com, you should avoid making a similar one, like examplemail.com.
Authenticate your IP addresses with SPF
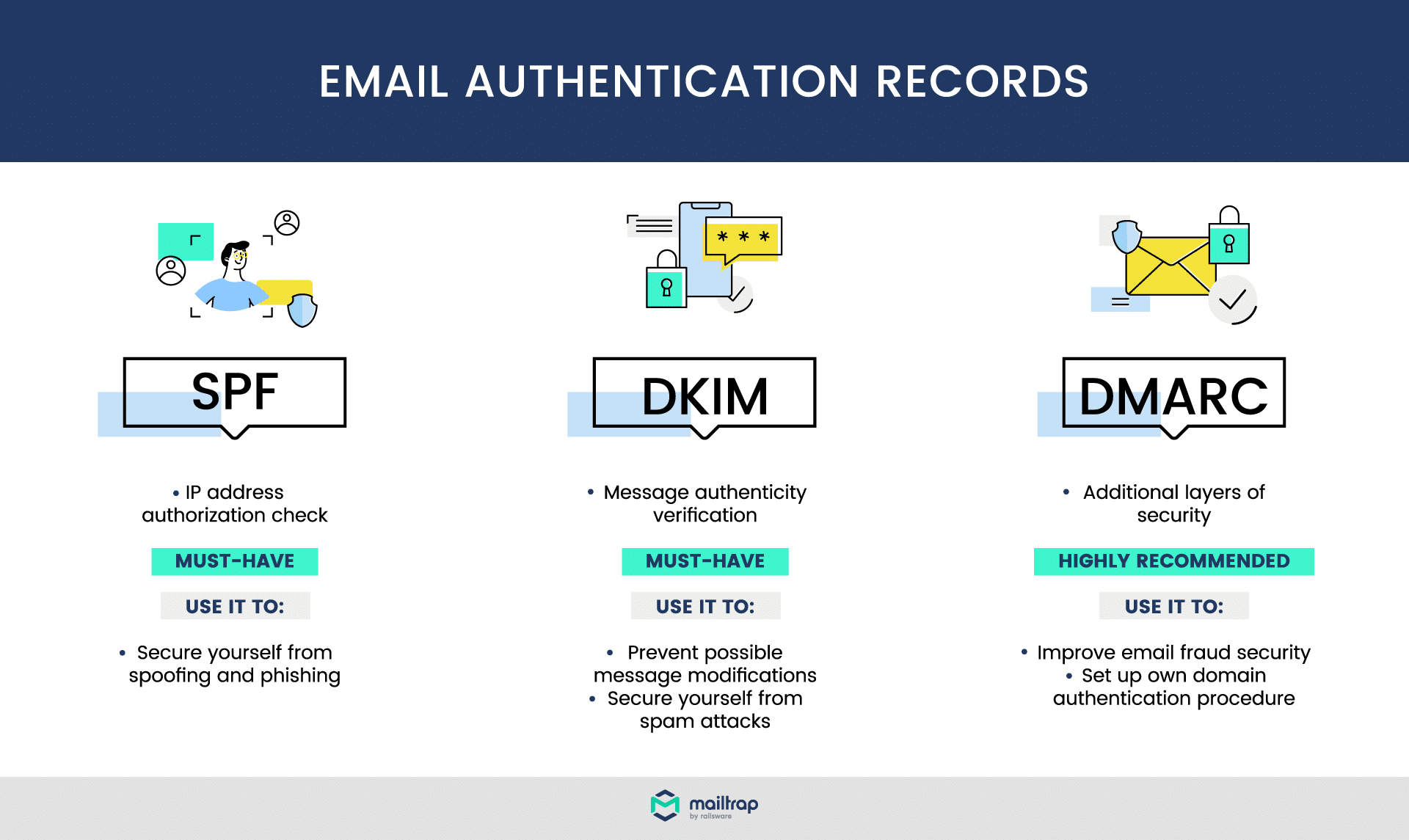
SPF stands for Sender Policy Framework, which is an internet standard that helps to prevent email fraud. The SPF record provides a list of authorized IP addresses that can send mail on behalf of the sender’s domain. An SPF record is a layer of protection in email infrastructure.
DMARC authentication
Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance (DMARC) is a protocol that uses SPF and DKIM to further prevent phishers from spoofing messages. A DMARC record is published alongside your DNS records and requires both SPF and DKIM to pass. DMARC lets you specify what should happen to any mail that appears to be spoofed. You can instruct receiving servers to block the message outright or put it in the spam folder.
Prepare for BIMI
"Brand Indicators for Message Identification" (BIMI) is the cherry on top of an already delicious cake. It reinforces trust with an extra step and builds a stronger connection between sender and recipient. When BIMI is activated, senders with a good reputation will be able to provide their business logo in the inbox so that recipients can easily identify the message as trustworthy.
BIMI is the only way to identify a company’s credibility. It is your only visual clue when it comes to finding out a message’s origin and authenticity. Check out our blog post on BIMI for more information.
Is your email being spoofed? We're here to help. Building trust with your subscribers is just as important as managing your reputation. Your subscribers want to know that their emails are coming from a genuine source and not a spoof, which will result in increased engagement. Let our team help you authenticate your email and build trust today!

Nadejda Milanova
An experienced Content creator in the field of Search Engine Optimization (SEO) and WordPress. A true proffesional with a Master's degree focused on journalism.
Read more by Nadejda Milanova