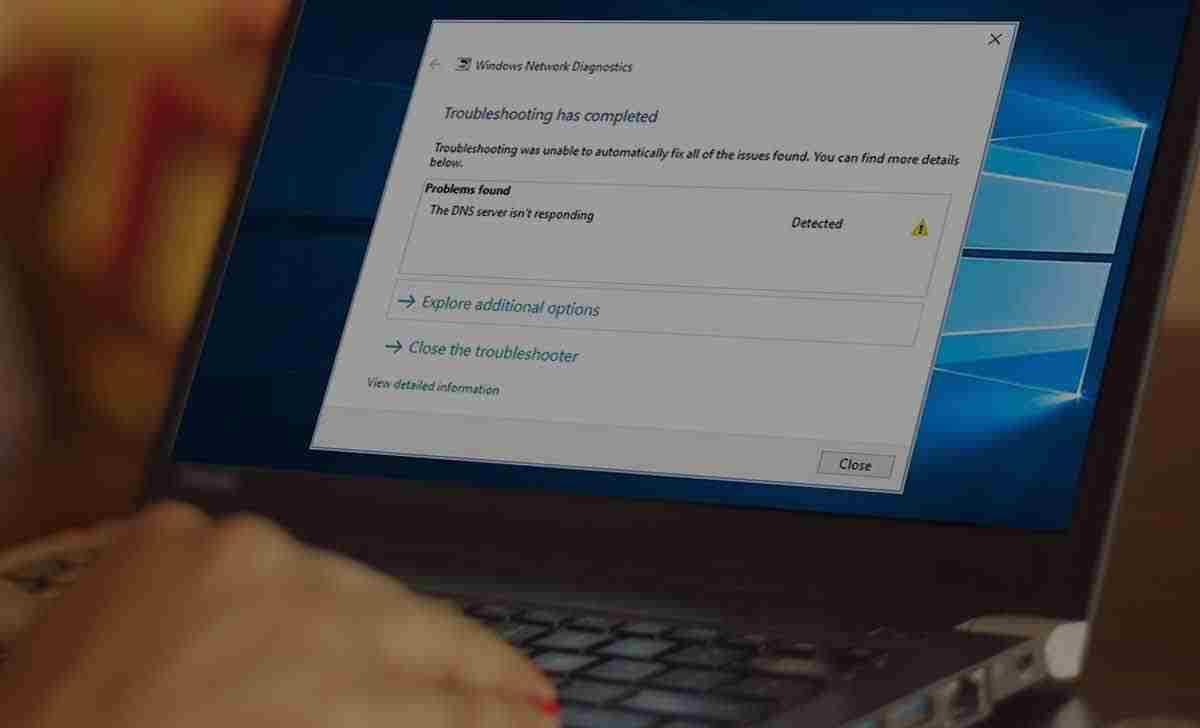
You are surfing the web and waiting for the next website to open, but instead the error "DNS server is not responding" appears. It has happened to almost all of us.
"DNS server not responding" is a problem that can have various causes, some of which are quick to resolve, others require a little more attention.
This guide will help you solve this problem step by step.
What is DNS?
DNS server: this is the server that allows the domain name to be stored (DNS - Domain Name System) and performs a "translation" between the IP address, formed by a series of numbers, to a domain name, which is easy we can use to search a website.
Information about IP addresses and domain names is stored on DNS servers. DNS is a distributed tree system of servers bound by a logical hierarchy. At the heart of this structure are the servers that store:
top-level domains - for example .com, .org, .edu, etc. and many country-level domains - .uk (for UK), .fi (for Finland), .fr (for France), etc. The next level is formed by the registered domains - about.com, etc. Local domains, also called subdomains, such as compnetworking.about.com, are defined and administered by the owners of the respective main domains. A dot (.) Is used to separate the different levels.
What does "DNS server not responding" mean? - The server hosting the site may be temporarily offline for technical reasons. - The computer's DNS service is corrupted or not working. - A firewall or other security software blocks access to a website or certain websites. - The modem / router is broken, not configured properly, or has an IP address conflict.
Determine the origin of the problem
If your DNS server does not respond, it does not necessarily need a technical repair.
Therefore, we first recommend that you try the following steps and find out what the problem is.
In case you can't connect to a specific site
To find out if DNS is a potential culprit when you have problems connecting to a specific site, first ping that site by sending the ping command to the command line as follows:
In the Start search engine type cmd and on the answer Command Promt right click on Run as Administrator. At the command prompt, type this command with the appropriate site that you want to check for a DNS problem.
ping ivytechnoweb.net
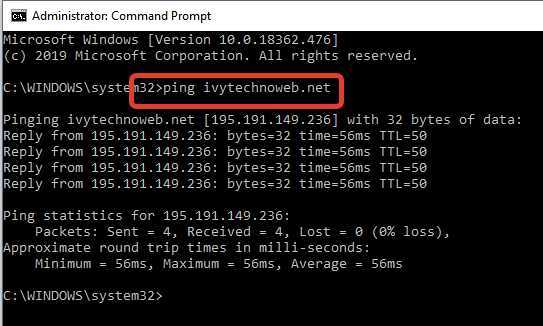
If the site is online, you will receive an answer like the one above. If not, you will receive the following answer:
Ping request could not find host.
Please check the name and try again.
If you ping a site and it's online, but you can't connect to it through your browser, the cause may be a DNS problem. If you suspect you have this problem, here's what you can do:
Internet connection speed testing
Check the speed of your internet connection, try disconnecting it and reconnecting after a minute of waiting.
There are many online services for checking the speed of your internet connection, such as Speedtest.
Try using a different browser
It seems trivial advice, but it is important to perform this very simple test. Try different browsers to open a website that doesn't suit you: Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Safari, Edge, Opera…
If the problem only applies to a browser, it means that its configuration is incorrect. The solution can be simple - uninstall and reinstall it.
Try connecting from another device
If connecting to a new network still indicates that the DNS server is not responding, try using your primary Internet connection, but with a different device to access the specified website. If you can connect to the website, then the problem is with your device. If not, then the problem is with the router or Internet Service Provider (ISP).
Try accessing the Internet using Network Safe Mode
Restart the computer and press the F8 key (or the appropriate one for your computer) at the first startup screen. If your computer has Internet access in safe mode with networking, then the problem may be caused by a firewall, security software, or a conflict between third-party antivirus software.
Disable the firewall or antivirus
To resolve this issue, try disabling the firewall, changing antivirus settings, or uninstalling the antivirus and anti-malware programs installed on your system.
If an error in the DNS server occurs only for some websites
If a DNS server error occurs for only some websites, then this may be a temporary problem for the server hosting those sites. You can check if websites are offline due to server problems using tools like uptrends.com. If after checking the site, it turns out that it is online and working, but you can not see it, then the problem is on your end.
Restart the modem and router
This is certainly the simplest and fastest method. Unplug your router and turn it back on after a few seconds or a minute.
Turn off unused networks
In most cases, the problem occurs when many networks are turned on. There are several ways to deactivate them -
Go to Control panel–> Network and Internet–> View network status and tasks–> Change adapter settings, or in the search engine type directly network connections, or press Windows + R, type ncpa.cpl–> Enter, or open Start and type ncpa.cpl in the search bar–> Enter.
After doing the above, the Network connections panel will open. Turn off all unused networks by simply right-clicking on them and selecting Disable.
Check the DNS assignments on the router
One of the security issues that can occur on the most common routers used for Internet connection of home users or small and medium enterprises is DNS hijacking - compromising the DNS set in the router with the addresses of malicious DNS servers.
This happens with Internet attacks that try to change the configuration of the router and take control of it. In this way, they direct sending to sites substitutes with completely different IP addresses, which probably have the same interface and appearance as the original sites, but contain malicious code.
This can also happen to sites that process sensitive data, such as online banking, insurance, healthcare, government, and more.
Therefore, it is essential to make sure that your router uses the correct DNS servers to avoid such attacks.
To do this, there is a website developed by F-secure (a well-known manufacturer of antivirus and other IT security products) that allows you to control the DNS settings of your router. Just contact at this address: f-secure.com
Resolved the "DNS server not responding" issue by properly configuring the network connection
Uninstall/reinstall network drivers
As a general rule, it is recommended that you create a restore point each time you install a new driver or apply a significant change to the operating system configuration.
An outdated or incompatible network card driver may cause connection problems. This can happen, for example, after updating Windows 10. Check Windows Update to see if a newer driver is available.
Here's how to update your network card driver:
In the search box on the taskbar, type Device Manager–> Device Manager from the list of results.
Browse Network adapters and find the one for your device.
Right-click Update driver–> Search automatically for updated driver software and then follow the instructions. If Windows does not find a new driver, you need to go to the computer manufacturer's website and download the latest network card driver from there. You need to know who the computer manufacturer is and the model name or number.
Reset TCP / IP
There may be a problem with your Internet connection settings as a result of some malware. In such cases, you can try to reset TCP / IP (Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol). How to do this with the help of the NetShell utility, see here. This will restore the IP addresses.
Again, type netsh winsock reset at the command prompt and press Enter.
This process is known as "winsock reset" or "comms reinstall".
Wait for the command line to go through the reset. When done, you will see the message "Winsock reset completed successfully".
Restart your computer to complete the action.
Even if resetting Winsock Reset is not directly related to the "DNS server is not responding" error, it would be useful to troubleshoot other Internet connection issues that may have caused the DNS problem.
Direct DNS cache
If your computer does not reach a specific website or server, the problem may be due to a damaged local DNS cache. Sometimes bad results are cached and therefore need to be cleared from the cache for your Windows computer to communicate properly with the host. Clearing the DNS cache can fix your internet connection problem. Here's how to clear the DNS cache:
Click Start and enter the word cmd in the search box. Then right-click on the command line icon and select Run as administrator.
In the window that opens, enter ipconfig / flushdns.
You should receive a confirmation message when the cache is cleared - Successfully flushed the DNS Resolver Cache.
Flushing the cache removes all the information stored in it, forcing the computer to find new DNS information.
Restart the computer and verify that the DNS problem is resolved.
Set DNS manually
You can enter DNS codes directly.
Open the Windows Run window by pressing Windows + R at the same time. Type:
ncpa.cpl
Find your internet connection and right-click to select Properties. Find the Internet Protocol version 4 (TCP / Ipv4) window in the Wi Fi Properties list, go to it to select it, and then go to the Properties button.
In the new Internet Protocol version 4 (TCP / Ipv4) Properties window, you can choose whether to use automatic IP and DNS or enter them manually.
Check "Use the following DNS server addresses":
Preferred DNS server: 8.8.8.8 Alternative DNS server: 8.8.4.4
These are Google's DNS servers and are useful because they allow you to work around the locks that may be set by your ISP. Many times the cause of the "DNS server does not respond" problem is censorship imposed by the provider.
Change the DNS server from the router Access the router's web addresses, usually http://192.168.1.1 Type this address in the browser. Once you enter the router's page, go to Settings. You have to find DNS somewhere in the settings.
In the DNS 1 or primary DNS field and in DNS 2 or secondary DNS, enter the addresses of the primary DNS server and the secondary DNS server that you want to use, respectively.
Check "Use the following DNS server addresses":
Preferred DNS server: 8.8.8.8 Alternative DNS server: 8.8.4.4
These are Google's DNS servers and are useful because they allow you to work around the locks that may be set by your ISP. Many times the cause of the "DNS server does not respond" problem is censorship imposed by the provider.
Conclusion
Now that you know the best possible "DNS server not responding" troubleshooting solutions, your problem should be resolved. If none of the above solutions work, the error may be caused by your ISP.

Nadejda Milanova
An experienced Content creator in the field of Search Engine Optimization (SEO) and WordPress. A true proffesional with a Master's degree focused on journalism.
Read more by Nadejda Milanova